 Sintered NdFeB magnets, i.e. sintered neodymium iron boron magnets, are those permanent magnetic materials based on a Nd-Fe-B tetragonal crystal structure. Sintered NdFeB magnets were invented by M. Sagawa’s team in the early 1980s, they are manufactured through a powder metallurgy process.
Sintered NdFeB magnets, i.e. sintered neodymium iron boron magnets, are those permanent magnetic materials based on a Nd-Fe-B tetragonal crystal structure. Sintered NdFeB magnets were invented by M. Sagawa’s team in the early 1980s, they are manufactured through a powder metallurgy process.
Sintered NdFeB magnets contain three basic elements neodymium, iron and boron. The neodymium element can be substituted by a portion of other rare earth elements including praseodymium, dysprosium, terbium, cerium, etc. The iron element can be substituted by a portion of cobalt element to increase the magnets’ Curie temperature Tc, thermal stability and corrosion resistance. In order to control the microstructure and the microchemistry so as to meet required performance, it also adds some doping elements including aluminium, copper, niobium, gallium, etc. For custom NdFeB magnets sintered, controlling the formula is the basic method to obtain required magnet grades.
Due to their outstanding magnetic properties (high remanence Br 1.1-1.5 T, middle high coercivity Hcj 800-3000 kA/m^3 and high maximum energy product (BH)max 220-430 kJ/m^3) together with competitive cost, sintered NdFeB magnets are widely applied in DC motors, servo motors, stepper/stepping motors, synchronous motors, linear motors, voice coil motors (VCMs), wind turbines and generators, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electric power steering (EPS), magnetic separation, etc.
Sintered NdFeB Magnets’ Grades and Their Magnetic Properties
| Grade | Br | Hcb | Hcj | (BH)max | Tw | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kGs | T | kOe | kA/m | kOe | kA/m | MGOe | kJ/m3 | ºC | |
| N52 | 14.2-14.8 | 1.42-1.48 | ≥10.5 | ≥836 | ≥11 | ≥876 | 50-53 | 398-422 | ≤80 |
| N50 | 13.9-14.4 | 1.39-1.44 | ≥10.8 | ≥859 | ≥12 | ≥955 | 48-51 | 382-406 | |
| N48 | 13.6-14.1 | 1.36-1.41 | ≥11.6 | ≥923 | 46-49 | 366-390 | |||
| N45 | 13.2-13.7 | 1.32-1.37 | ≥11.6 | ≥923 | 43-46 | 342-366 | |||
| N42 | 12.8-13.3 | 1.28-1.33 | ≥11.4 | ≥907 | 40-43 | 318-342 | |||
| N40 | 12.4-12.9 | 1.24-1.29 | ≥11.4 | ≥907 | 38-41 | 302-326 | |||
| N38 | 12.1-12.6 | 1.21-1.26 | ≥11.2 | ≥891 | 36-39 | 286-310 | |||
| N35 | 11.7-12.2 | 1.17-1.22 | ≥10.8 | ≥859 | 33-36 | 263-286 | |||
| N33 | 11.3-11.8 | 1.13-1.18 | ≥10.5 | ≥836 | 31-34 | 247-271 | |||
| N30 | 10.8-11.3 | 1.08-1.13 | ≥10.0 | ≥796 | 28-31 | 223-247 | |||
| N50M | 13.9-14.4 | 1.39-1.44 | ≥13.0 | ≥1035 | ≥13 | ≥1035 | 48-51 | 382-406 | ≤100 |
| N48M | 13.6-14.1 | 1.36-1.41 | ≥12.8 | ≥1019 | ≥14 | ≥1114 | 46-49 | 366-390 | |
| N45M | 13.2-13.7 | 1.32-1.37 | ≥12.5 | ≥995 | 43-46 | 342-366 | |||
| N42M | 12.8-13.3 | 1.28-1.33 | ≥12.0 | ≥955 | 40-43 | 318-342 | |||
| N40M | 12.4-12.9 | 1.24-1.29 | ≥11.6 | ≥923 | 38-41 | 302-326 | |||
| N38M | 12.1-12.6 | 1.21-1.26 | ≥11.3 | ≥899 | 36-39 | 286-310 | |||
| N35M | 11.7-12.2 | 1.17-1.22 | ≥10.9 | ≥867 | 33-36 | 263-286 | |||
| N33M | 11.3-11.8 | 1.13-1.18 | ≥10.5 | ≥836 | 31-34 | 247-271 | |||
| N30M | 10.8-11.3 | 1.08-1.13 | ≥10.0 | ≥796 | 28-31 | 223-247 | |||
| N50H | 13.9-14.4 | 1.39-1.44 | ≥13.0 | ≥1035 | ≥16 | ≥1273 | 48-51 | 382-406 | ≤120 |
| N48H | 13.6-14.1 | 1.36-1.41 | ≥12.8 | ≥1019 | ≥17 | ≥1353 | 46-49 | 366-390 | |
| N45H | 13.2-13.7 | 1.32-1.37 | ≥12.5 | ≥995 | 43-46 | 342-366 | |||
| N42H | 12.8-13.3 | 1.28-1.33 | ≥12.0 | ≥955 | 40-43 | 318-342 | |||
| N40H | 12.4-12.9 | 1.24-1.29 | ≥11.6 | ≥923 | 38-41 | 302-326 | |||
| N38H | 12.1-12.6 | 1.21-1.26 | ≥11.3 | ≥899 | 36-39 | 286-310 | |||
| N35H | 11.7-12.2 | 1.17-1.22 | ≥10.9 | ≥867 | 33-36 | 263-286 | |||
| N33H | 11.3-11.8 | 1.13-1.18 | ≥10.5 | ≥836 | 31-34 | 247-271 | |||
| N30H | 10.8-11.3 | 1.08-1.13 | ≥10.0 | ≥796 | 28-31 | 223-247 | |||
| N48SH | 13.6-14.1 | 1.36-1.41 | ≥12.8 | ≥1019 | ≥20 | ≥1592 | 46-49 | 366-390 | ≤150 |
| N45SH | 13.2-13.7 | 1.32-1.37 | ≥12.5 | ≥995 | 43-46 | 342-366 | |||
| N42SH | 12.8-13.3 | 1.28-1.33 | ≥12.0 | ≥955 | 40-43 | 318-342 | |||
| N40SH | 12.4-12.9 | 1.24-1.29 | ≥11.6 | ≥923 | 38-41 | 302-326 | |||
| N38SH | 12.1-12.6 | 1.21-1.26 | ≥11.3 | ≥899 | 36-39 | 286-310 | |||
| N35SH | 11.7-12.2 | 1.17-1.22 | ≥10.9 | ≥867 | 33-36 | 263-286 | |||
| N33SH | 11.3-11.8 | 1.13-1.18 | ≥10.5 | ≥836 | 31-34 | 247-271 | |||
| N30SH | 10.8-11.3 | 1.08-1.13 | ≥10.0 | ≥796 | 28-31 | 223-247 | |||
| N42UH | 12.8-13.3 | 1.28-1.33 | ≥12.2 | ≥971 | ≥25 | ≥1990 | 40-43 | 318-342 | ≤180 |
| N40UH | 12.4-12.9 | 1.24-1.29 | ≥11.8 | ≥939 | 38-41 | 302-326 | |||
| N38UH | 12.1-12.6 | 1.21-1.26 | ≥11.5 | ≥915 | 36-39 | 286-310 | |||
| N35UH | 11.7-12.2 | 1.17-1.22 | ≥11.1 | ≥883 | 33-36 | 263-286 | |||
| N33UH | 11.3-11.8 | 1.13-1.18 | ≥10.7 | ≥851 | 31-34 | 247-271 | |||
| N30UH | 10.8-11.3 | 1.08-1.13 | ≥10.2 | ≥812 | 28-31 | 223-247 | |||
| N40EH | 12.4-12.9 | 1.24-1.29 | ≥11.8 | ≥939 | ≥30 | ≥2388 | 38-41 | 302-326 | ≤200 |
| N38EH | 12.1-12.6 | 1.21-1.26 | ≥11.5 | ≥915 | 36-39 | 286-310 | |||
| N35EH | 11.7-12.2 | 1.17-1.22 | ≥11.1 | ≥883 | 33-36 | 263-286 | |||
| N33EH | 11.3-11.8 | 1.13-1.18 | ≥10.7 | ≥851 | 31-34 | 247-271 | |||
| N30EH | 10.8-11.3 | 1.08-1.13 | ≥10.2 | ≥812 | 28-31 | 223-247 | |||
| N35AH | 11.7-12.2 | 1.17-1.22 | ≥11.1 | ≥883 | ≥35 | ≥2786 | 33-36 | 263-286 | ≤230 |
| N33AH | 11.3-11.8 | 1.13-1.18 | ≥10.7 | ≥851 | 31-34 | 247-271 | |||
| N30AH | 10.8-11.3 | 1.08-1.13 | ≥10.2 | ≥812 | 28-31 | 223-247 | |||
| N28AH | 10.4-10.9 | 1.04-1.09 | ≥9.8 | ≥780 | 26-29 | 207-231 | |||
Note:
∗ The data in the above table were samples’ results tested at the temperature of 20 °C.
∗ The temperature coefficients of Br and Hcj are α(Br): -0.09~-0.12 %/ºC and β(Hcj): -0.40~-0.60 %/ºC, respectively.
∗ The above data are only for reference, magnets can be tailored according to customers’ personalized requirements.
Sintered NdFeB Magnets’ Shapes, Magnetization Direction and Size Range
| Shape | Graphic Description | Magnetization Direction | Size Range | |
| Disc/Cylinder Magnet | 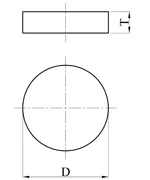 | 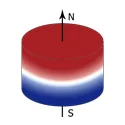 | Axially Magnetized | D: 1-100 mm |
| T: 0.5-100 mm | ||||
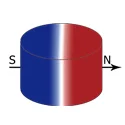 | Diametrically Magnetized | D: 1-100 mm | ||
| T: 0.5-100 mm | ||||
| Ring Magnet | 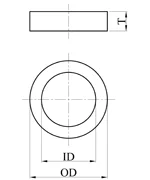 | 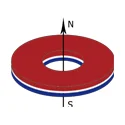 | Axially Magnetized | OD: 4-100 mm |
| ID: 1-90 mm | ||||
| T: 1-60 mm | ||||
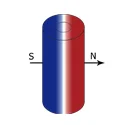 | Diametrically Magnetized | OD: 4-100 mm | ||
| ID: 1-90 mm | ||||
| T: 1-60 mm | ||||
 | Radially Magnetized | OD: 24-200 mm | ||
| ID: 18-180 mm | ||||
| T: 5-60 mm | ||||
| Block/Rectangular Magnet |  | 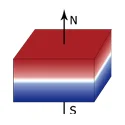 | Thickness Magnetized | L: 1-160 mm |
| W: 1-100 mm | ||||
| T: 1-100 mm | ||||
| Arc/Segment Magnet | 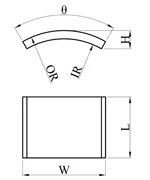 | 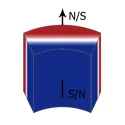 | Diametrically Magnetized | OD-ID≥1 mm |
| L: 1-160 mm | ||||
| W: 3-100 mm | ||||
| H: 1-80 mm | ||||
Note:
∗ Other shapes of sintered NdFeB magnets can also be tailored according to customers’ specific requirements.
Sintered NdFeB Magnets' Coatings
| Coating | Thickness (μm) | SST (hr) | PCT (hr) | Tw (ºC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn (Zinc) | 5-15 | >24 | - | ≤160 |
| C-Zn (Colored Zinc) | 5-15 | >48 | - | ≤160 |
| Electroless Nickel | 10-30 | >96 | >72 | ≤230 |
| NiCuNi (Nickel Copper Nickel) | 10-20 | >48 | >48 | ≤230 |
| NiCu + Black Nickel | 10-20 | >48 | >72 | ≤230 |
| NiCuNi + Tin | 10-25 | >48 | >48 | ≤160 |
| NiCuNi + Gold | 10-25 | >48 | >48 | ≤230 |
| NiCuNi + Silver | 10-25 | >48 | >48 | ≤160 |
| Epoxy | 10-30 | >72 | >48 | ≤160 |
| Teflon | 10-20 | >48 | - | ≤230 |
| Everlube | 10-20 | >96 | >72 | ≤230 |
| Parylene | 0.2-5 | >96 | - | ≤230 |
Note:
∗ Salt spray test (SST) was conducted at 35 ºC with 5% NaCl solution.
∗ Pressure cooker test (PCT) was conducted at 120 ºC, 2 atm and 100% RH.
Sintered NdFeB Magnets Physical Properties
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Density (ρ) | g/cm3 | 7.4-7.7 |
| Curie Temperature (Tc) | ºC | 310-370 |
| Recoil Permeability (μrec) | - | 1.05 |
| Vickers Hardness (HV) | MPa | 500-600 |
| Bending Strength (σbb) | MPa | 200-400 |
| Compressive Strenght (σbc) | MPa | 1000-1100 |
| Tensile Strength (σb) | MPa | 80-90 |
| Resistivity (ρ) | μΩ·m | 1.4-1.6 |
| Thermal Conductivity (λ) | W/(m·K) | 8-10 |
| Young's Modulus (E) | GPa | 150-200 |
| Thermal Expansivity ∥ Magnetization (α∥) | 10-6/ºC | 3-4 |
| Thermal Expansivity ⊥ Magnetization (α⊥) | 10-6/ºC | 1-3 |
Note:
∗ The above data are only for reference, specific magnets maybe have different values.
Downloads
Introduction to Basic Composition and Microstructure of Sintered NdFeB Magnet
What is the Difference between N35 and N52 Magnets?
What is the Strongest Commercial Permanent Magnet in the World?
How to Magnetize and Demagnetize a Permanent Magnet, respectively?
Do Permanent Magnets ever Lose Their Magnetism or Get Weaker?
