What is a Permanent Magnet?
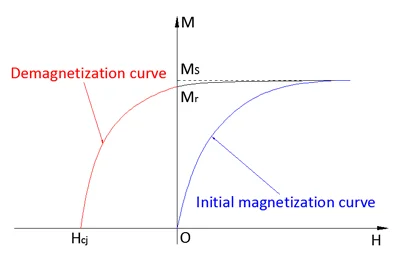
A permanent magnet is a material that is able to provide magnetic flux when magnetized with an applied magnetic field. The ability is characterized by two key parameters: remanence and coercivity. Generally, a permanent magnet’s intrinsic coercivity (Hcj) is higher than 300kOe (in CGS unit) or 24kA/m (in SI unit). With higher coervivity, a permanent magnet has higher ability to resist demagnetization, including field demagnetization from the electric or magnetic circuit and thermal demagnetization from the working temperature in various motors and/or electric machines applications.
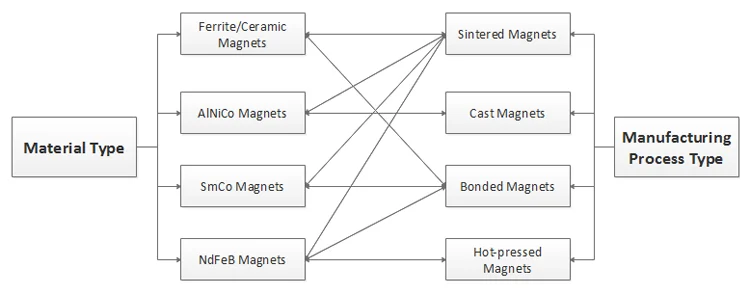
A commercial permanent magnet requires relatively high remanence and coercivity at an affordable cost. In regards to material types, commercial permanent magnets include ferrite/ceramic, AlNiCo, SmCo and NdFeB magnets. In regards to manufacturing processes, they include sintered, cast, bonded (compressed, injected, extruded and calendered) and hot-pressed magnets.